Understanding the complexities of cancer requires a multi-faceted approach, and one of the most powerful tools in this quest is the integration of omics technologies. By delving into the depths of the genome, epigenome, transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome, researchers are able to unravel the intricate layers of cancer biology. This article will take you on a journey through the world of cancer omics, exploring how these technologies are revolutionizing our understanding of cancer and paving the way for precision medicine.
What are Cancer Omics?

Cancer omics refers to the study of the various types of omics data that can be generated from cancer samples. Omics is a suffix that denotes the study of a particular type of data, such as genomics, epigenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. Each of these omics provides a unique perspective on cancer, allowing researchers to gain a comprehensive understanding of the disease.
The Genome: The Blueprint of Life
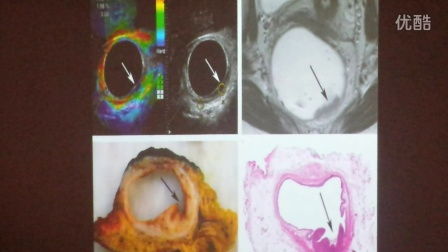
The genome is the complete set of genetic instructions for an organism, and it plays a crucial role in cancer development. By analyzing the genome of cancer cells, researchers can identify mutations that drive tumor growth and progression. This information can be used to develop targeted therapies that specifically target these mutations, leading to more effective and personalized treatment options.
| Genome Sequencing | Identifies mutations | Enables targeted therapies |
|---|---|---|
| Copy Number Variation Analysis | Identifies gene amplifications and deletions | Helps predict prognosis and treatment response |
The Epigenome: The Mysterious Layers of Regulation
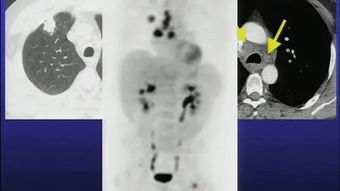
The epigenome refers to the chemical modifications that can be added to DNA and histone proteins, which can affect gene expression without changing the underlying DNA sequence. Epigenetic changes are often associated with cancer development and progression, and they can be influenced by environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and genetic predisposition. By studying the epigenome, researchers can identify potential targets for cancer prevention and treatment.
The Transcriptome: The Language of the Cell
The transcriptome is the collection of all RNA molecules present in a cell at a given time. By analyzing the transcriptome, researchers can identify genes that are turned on or off in cancer cells, providing insights into the molecular pathways that drive tumor growth and progression. This information can be used to develop new diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies.
The Proteome: The Workforce of the Cell
The proteome is the collection of all proteins present in a cell. Proteins are the building blocks of cells and play a crucial role in various cellular processes. By studying the proteome, researchers can identify proteins that are overexpressed or underexpressed in cancer cells, providing insights into the molecular mechanisms of cancer development and progression. This information can be used to develop new diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies.
The Metabolome: The Fuel of the Cell
The metabolome is the collection of all small molecules present in a cell. Metabolites are the building blocks of larger molecules and play a crucial role in various cellular processes. By studying the metabolome, researchers can identify metabolic changes that occur in cancer cells, providing insights into the metabolic pathways that drive tumor growth and progression. This information can be used to develop new diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies.
The Power of Multi-Omics Analysis
The integration of cancer omics data provides a powerful tool for understanding the complexities of cancer. By combining information from multiple omics layers, researchers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the disease and identify potential therapeutic targets. This approach has already led to the development of several new diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies, and it is expected to continue to revolutionize cancer research and treatment.
In conclusion, cancer omics is a rapidly evolving field that is transforming our understanding of cancer and paving the way for precision medicine. By delving into the depths of the genome, epigenome, transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome, researchers are able to unravel the intricate layers of cancer biology and develop new diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies that can improve patient outcomes.
