Cellular Respiration: The Life-Sustaining Process
Cellular respiration is a fundamental biological process that occurs within the cells of all living organisms. It is the process by which cells convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. This process is crucial for the survival of organisms, as it provides the energy needed for various cellular activities. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of cellular respiration, exploring its stages, importance, and the role of different molecules involved.
Stages of Cellular Respiration

The process of cellular respiration can be divided into three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation. Let’s take a closer look at each stage.
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. During this stage, glucose, a six-carbon sugar, is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon compound. This process yields a small amount of ATP and NADH, which is a high-energy electron carrier.
The Citric Acid Cycle takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. In this stage, the two molecules of pyruvate produced during glycolysis are further broken down, releasing carbon dioxide and producing ATP, NADH, and FADH2. The citric acid cycle is a series of enzyme-mediated reactions that generate energy-rich molecules and provide the electrons needed for the next stage of cellular respiration.
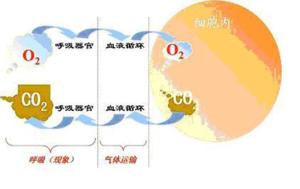
Oxidative Phosphorylation is the final stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This stage involves the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to a series of proteins embedded in the membrane, known as the electron transport chain. As electrons move through the chain, energy is released and used to pump protons across the membrane, creating a gradient. This gradient drives the synthesis of ATP through a process called chemiosmosis.
Importance of Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is essential for the survival of all living organisms. Here are some key reasons why this process is so important:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Production | Cellular respiration generates ATP, the primary energy currency of the cell, which is used for various cellular activities such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis. |
| Waste Removal | During cellular respiration, carbon dioxide and water are produced as waste products. These waste products are then eliminated from the body through exhalation and excretion, respectively. |
| Metabolic Regulation | Cellular respiration is tightly regulated to ensure that the energy needs of the cell are met. This regulation helps maintain homeostasis and allows cells to adapt to changing conditions. |
Role of Molecules in Cellular Respiration
Several molecules play crucial roles in the process of cellular respiration. Here are some of the key molecules involved:


